Welcome to my blog, a place to share information, experiences, thoughts and ideas with my methodology students from Instituto Valle Central Sede Toesca Santiago de Chile. Feel free to add comments and ask questions about our class.
Saturday, October 27, 2012
Friday, October 26, 2012
Saturday, October 6, 2012
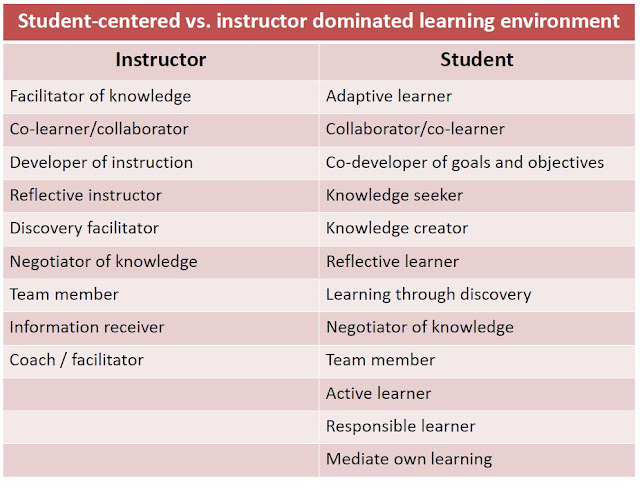
Constructivism: A Holistic Approach to Teaching and Learning
A definition of constructivism
Fundamentally, constructivism says that people construct their own understanding and knowledge of the world through experiencing things and reflecting on those experiences.
Constructivism is a learning theory
- Learning is an active process
- Knowledge is constructed from (and shaped by) experience
- Learning is a personal interpretation of the world
- Emphasizes problem solving and understanding
- Uses authentic tasks, experiences, settings, assessments
- Content presented holistically –not in separate smaller parts
Constructivism is a process –the instructor
- Adapt curriculum to address students’ suppositions
- Help negotiate goals and objectives with learners
- Pose problems of emerging relevance to students
- Emphasize hands‐on, real‐world experiences
- Seek and value students’ points of view
- Use the social context of content
- Provide multiple modes of representations / perspectives on content
- Create new understandings via coaching, moderating , suggesting
- Testing should be integrated with the task and not a separate activity
- Use errors to inform students of progress to understanding and changes in ideas
Constructivism is a process –the student
- Help develop own goals and assessments
- Create new understandings (via coaching, moderating, suggesting)
- Control learning (reflecting)
- Member of community of learners
- Collaborate among fellow students
- Learn in a social experience –appreciate different perspectives
- Take ownership and voice in learning process
Constructivism is an instructional strategy
- Involves collaboration between instructors, students and others (community members)
- Tailored to needs and purposes of individual learners
- Features active, challenging, authentic and multidisciplinary learning
- Constructivism can help students
– Use and develop his or her abilities
– Build on his or her prior knowledge and experiences
– Develop life‐long learning
– Preferred learning style
– Rate of learning
– Personal interactions with other learners
Applying constructivism in the classroom
Constructivism summary
- Constructivism encourages instructors to provide for each student’s
– Preferred learning style
– Rate of learning
– Personal interactions with other learners
Applying constructivism in the classroom
- Pose problems that are or will be relevant to students
- Structure learning around essential concepts
- Be aware that students’ points of view are windows into their reasoning
- Adapt teaching to address students’ suppositions and development
- Assess student learning in context of teaching
Constructivism summary
- Shifts emphasis from teaching to learning
- Individualizes and contextualizes students’ learning experiences
- Helps students develop processes, skills and attitudes
- Considers students’ learning styles
- Focuses on knowledge construction, not reproduction
- Uses authentic tasks to engage learners
- Provides for meaningful, problem‐based thinking
- Requires negotiation of meaning
- Requires reflection of prior and new knowledge
- Extends students beyond content presented to them
Wednesday, October 3, 2012
Tuesday, October 2, 2012
For you to prepare the test.
Write T (true)
or F (false) according to the statement.
1.- ______The method
concept in language teaching is the notion of a systematic set of teaching
practices based on a particular theory of language and language learning.
2.- ______ According
to Vygotsky, children
construct knowledge from actively interacting with the physical
environment in developmental stages.
3.- ______ Parents who scaffolded effectively kept child “on task”
by reminding him of the purpose or goal.
4.- ______ Very young learners are not able to organize
their learning.
5.- ______ Young learners can not work with others and learn from
others.
6.- ______ An approach is an ordered sequence of techniques.
7.- ______ In PPP, the teacher introduces a situation which
contextualizes the language to be taught.
8.- ______ In communicative
activities there is no teacher intervention.
9.- ______ Three basic
stages of Task based learning are pre production, early production and speech
emergence.
10.- ______ According to Asher, 2nd language learning could have similar
developmental patterns to that of child acquisition.
11.- ______ Communicative Language Teaching
advocates that learners learn a language through using it to communicate.
12.- ______ The
teacher’s role in TPR is being a commander and action monitor.
13.- ______ Communicative
competence is the progressive acquisition of the ability to use a language to
achieve one's communicative purpose.
14.- ______ During the step 2 in TPR, the teacher says the
command as both the teacher and the students then perform the action.
15.- ______ In a communicative classroom the instructor corrects speech
errors directly.
16.- ______ Single/two-word answers are an example of speech emergence.
17.- ______ L1 is acquired and L2 is learned.
18.- ______ Pre production is the silent period.
19.- ______ In early production, children have a limited vocabulary and
respond in short phrases or sentences.
20.- ______ If a teacher presents the language orally; the child reads.
21.- ______ The lexical approach says that language doesn't consist of
phrases, collocations, and idioms, but also
traditional grammar and
vocabulary.
22.- ______ One of the principles
of TPR states that feelings of success and low anxiety facilitate learning.
23.- ______ Bruner focused on
the importance of language in a child’s cognitive development
24.- ______ The best material in the Natural Approach is realia.
More Finger Puppets
Finger Puppets by Ruben Ramírez
Finger Puppets by Lucía Núñez
Finger Puppets by Marjorie Sánchez
Finger Puppets by Roberto Aros
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)





.jpg)

