A definition of constructivism
Fundamentally, constructivism says that people construct their own understanding and knowledge of the world through experiencing things and reflecting on those experiences.
Constructivism is a learning theory
- Learning is an active process
- Knowledge is constructed from (and shaped by) experience
- Learning is a personal interpretation of the world
- Emphasizes problem solving and understanding
- Uses authentic tasks, experiences, settings, assessments
- Content presented holistically –not in separate smaller parts
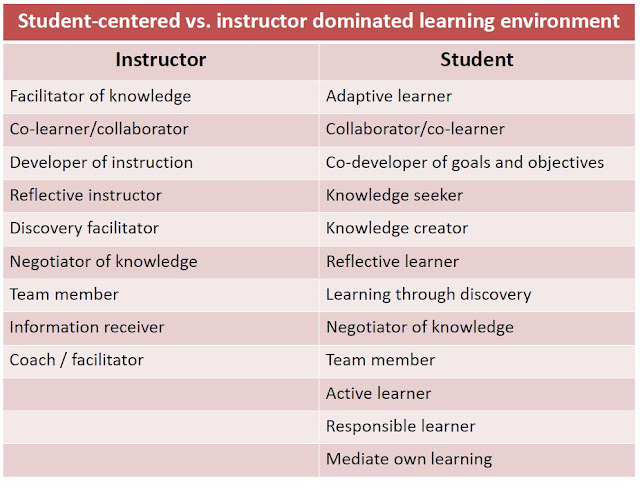
Constructivism is a process –the instructor
- Adapt curriculum to address students’ suppositions
- Help negotiate goals and objectives with learners
- Pose problems of emerging relevance to students
- Emphasize hands‐on, real‐world experiences
- Seek and value students’ points of view
- Use the social context of content
- Provide multiple modes of representations / perspectives on content
- Create new understandings via coaching, moderating , suggesting
- Testing should be integrated with the task and not a separate activity
- Use errors to inform students of progress to understanding and changes in ideas
Constructivism is a process –the student
- Help develop own goals and assessments
- Create new understandings (via coaching, moderating, suggesting)
- Control learning (reflecting)
- Member of community of learners
- Collaborate among fellow students
- Learn in a social experience –appreciate different perspectives
- Take ownership and voice in learning process
Constructivism is an instructional strategy
- Involves collaboration between instructors, students and others (community members)
- Tailored to needs and purposes of individual learners
- Features active, challenging, authentic and multidisciplinary learning
- Constructivism can help students
– Use and develop his or her abilities
– Build on his or her prior knowledge and experiences
– Develop life‐long learning
– Preferred learning style
– Rate of learning
– Personal interactions with other learners
Applying constructivism in the classroom
Constructivism summary
- Constructivism encourages instructors to provide for each student’s
– Preferred learning style
– Rate of learning
– Personal interactions with other learners
Applying constructivism in the classroom
- Pose problems that are or will be relevant to students
- Structure learning around essential concepts
- Be aware that students’ points of view are windows into their reasoning
- Adapt teaching to address students’ suppositions and development
- Assess student learning in context of teaching
Constructivism summary
- Shifts emphasis from teaching to learning
- Individualizes and contextualizes students’ learning experiences
- Helps students develop processes, skills and attitudes
- Considers students’ learning styles
- Focuses on knowledge construction, not reproduction
- Uses authentic tasks to engage learners
- Provides for meaningful, problem‐based thinking
- Requires negotiation of meaning
- Requires reflection of prior and new knowledge
- Extends students beyond content presented to them

No comments:
Post a Comment